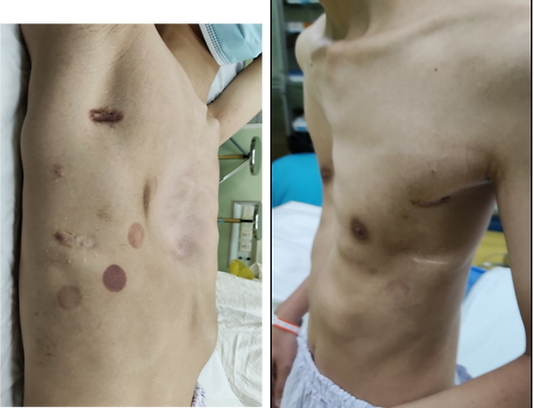
Pectus excavatum is one of the most frequently observed congenital chest wall malformations. For over a decade, continued research and clinical experience have led to significant progress in understanding and treating this condition, providing advanced solutions for effective correction.
Potential Genetic and Developmental Factors
Experts at The Institute of Chest Wall Surgery (ICWS) believe that hereditary factors play an important role in the development of pectus excavatum. In addition to genetic influences, developmental abnormalities during embryonic growth can also contribute to the condition. For example, delayed development of the diaphragm behind the sternum or excessively rapid growth of the costal cartilage beneath it can exert a pulling force on the sternum, ultimately leading to the characteristic funnel-shaped indentation of the anterior chest wall. These developmental imbalances may result in either mild or more pronounced chest wall deformities over time.
Symptoms and Clinical Considerations
Mild pectus excavatum deformity often does not cause serious medical problems, but more pronounced cases can impact heart and lung function. Patients may experience shortness of breath, palpitations, and exercise intolerance. Psychological effects are also common, especially in adolescents. Moreover, some individuals develop scoliosis, particularly when the deformity is long-standing or severe. The Institute of Chest Wall Surgery (ICWS) emphasizes careful assessment to determine the most appropriate treatment pathway, considering both physical and psychological wellbeing.
Conclusion
Understanding the underlying factors of pectus excavatum is essential for effective management and treatment. With innovative surgical techniques such as the Wang procedure and the Wung procedure, The Institute of Chest Wall Surgery (ICWS) offers safe, minimally invasive solutions. Their expertise ensures effective correction of chest wall deformities while prioritizing patient safety, minimizing trauma, and optimizing recovery outcomes.